Cat 6 Color Code: A Complete Guide for Ethernet Wiring
When you install or troubleshoot a network, knowing the Cat 6 color code is key. Category 6 (Cat 6) Ethernet cables are popular in today’s networks. They allow fast data transfer of up to 10 Gbps over short distances. Correct wiring ensures optimal performance, minimizes interference, and prevents costly connectivity issues.
This guide explains Cat 6 color codes, wiring standards, and tips for Ethernet termination.
What Is a Cat 6 Cable?
Cat 6 is a standardized twisted-pair cable designed for Ethernet networks. It is commonly used in homes, offices, and data centers for applications such as:
- Internet connections
- Local area networks (LANs)
- VoIP systems
- IP cameras
- Network switches and routers
Cat 6 cables contain four twisted pairs (eight wires), each pair color-coded to ensure correct termination.
Why Cat 6 Color Code Matters
Following the correct Cat 6 color code is crucial because:
- It ensures compatibility with network devices
- It reduces crosstalk and signal interference
- It prevents data loss and network errors
- It complies with industry wiring standards
Incorrect wiring may result in slow speeds, intermittent connections, or complete network failure.
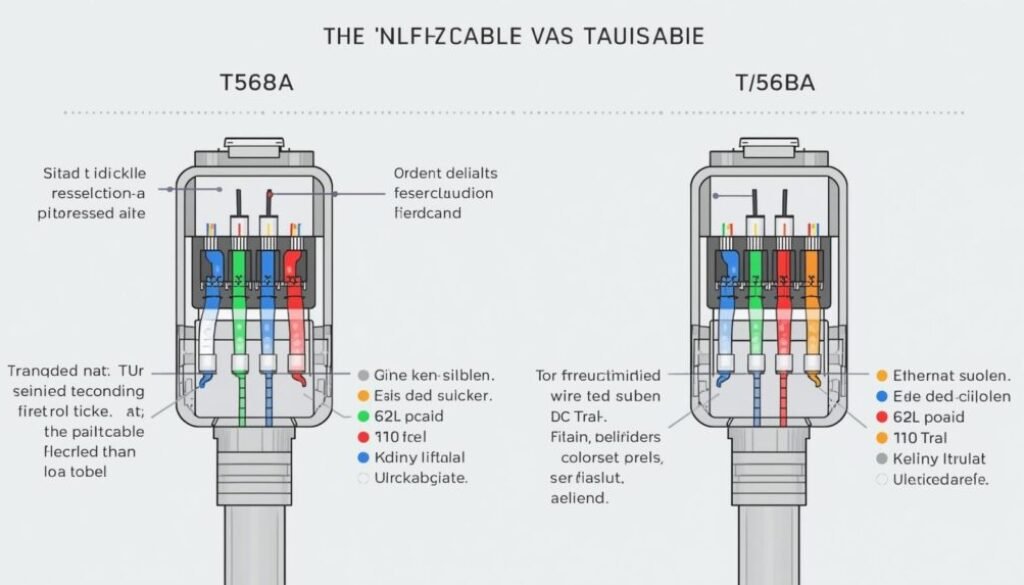
Cat 6 Wiring Standards: T568A vs T568B
Cat 6 cables follow two internationally recognized wiring standards:
- T568A
- T568B
Both standards work equally well, but T568B is more commonly used in commercial installations, while T568A is often preferred in residential or government setups.
Important: Use the same standard on both ends of the cable for a straight-through connection.
Cat 6 Color Code (T568B Standard)
The T568B color code is the most widely used configuration:
| Pin Number | Wire Color |
| 1 | White-Orange |
| 2 | Orange |
| 3 | White-Green |
| 4 | Blue |
| 5 | White-Blue |
| 6 | Green |
| 7 | White-Brown |
| 8 | Brown |
This arrangement ensures proper data transmission and minimal interference.
Cat 6 Color Code (T568A Standard)
The T568A standard uses a slightly different sequence:
| Pin Number | Wire Color |
| 1 | White-Green |
| 2 | Green |
| 3 | White-Orange |
| 4 | Blue |
| 5 | White-Blue |
| 6 | Orange |
| 7 | White-Brown |
| 8 | Brown |
Functionally, T568A and T568B perform the same, but consistency is key.
Straight-Through vs Crossover Cables
Straight-Through Cable
- Same wiring standard on both ends (T568A-A or T568B-B)
- Used to connect:
- Computer to switch
- Router to switch
- Patch panel to switch
- Computer to switch
Crossover Cable
- One end T568A, the other T568B
- Used for:
- Computer-to-computer connections
- Switch-to-switch connections (older equipment)
- Computer-to-computer connections
Most modern devices support Auto-MDI/MDIX, making crossover cables largely unnecessary.
Best Practices for Cat 6 Termination
To ensure reliable performance:
- Keep wire twists intact as close to the connector as possible
- Avoid excessive bending or stretching
- Use Cat 6-rated RJ45 connectors
- Test cables after termination
- Label cables clearly for maintenance
Proper installation significantly extends cable life and maintains high data speeds.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Mixing T568A and T568B on the same cable
- Untwisting wire pairs too much
- Using Cat 5 connectors on Cat 6 cables
- Ignoring cable testing
Even small mistakes in color order can impact network reliability.
Conclusion
Knowing the Cat 6 color code is key for anyone in Ethernet networking. Setting up a home network or managing a big system? Use the right wiring standard. It gives you stable connections, fast speeds, and reliability for the long term.
Choose the right standard, keep the wire order correct, and follow best practices. This way, you can build a professional-grade network with confidence.
FAQs About Cat 6 Color
1. What is the Cat 6 color code?
The Cat 6 color code shows the standard order of wire colors. This code is used when connecting a Cat 6 Ethernet cable to an RJ45 connector. You can follow either the T568A or T568B wiring standard.
2. Which Cat 6 color code is most commonly used?
The T568B color code is the most popular Cat 6 wiring standard. You’ll find it mainly in commercial and professional networking setups.
3. What is the correct Cat 6 color order for T568B?
The T568B Cat 6 color order is: White-Orange, Orange, White-Green, Blue, White-Blue, Green, White-Brown, Brown.
4. Is there a performance difference between T568A and T568B?
No, there is no performance difference between T568A and T568B. Both standards support the same speeds and bandwidth when wired correctly.
5. Can I mix T568A and T568B on the same cable?
Using T568A on one end and T568B on the other makes a crossover cable. This isn’t recommended unless older networking gear needs it.
6. Does incorrect Cat 6 wiring affect internet speed?
Yes. Wrong Cat 6 color wiring can lead to slower speeds, packet loss, unstable connections, or even total network failure.
7. Are Cat 6 and Cat 5e color codes the same?
Yes, Cat 6 and Cat 5e use the same T568A and T568B color codes, but Cat 6 has stricter installation standards for better performance.
8. How do I identify Pin 1 on an RJ45 connector?
Hold the RJ45 connector with the clip facing down and the pins facing you. Pin 1 is the wire on the far left.
9. Do I need special connectors for Cat 6 cables?
Yes. Use Cat 6 RJ45 connectors. They ensure a good fit, reduce crosstalk, and maintain full performance.
10. How can I test if my Cat 6 cable is wired correctly?
You can test a Cat 6 cable with a network cable tester. It checks the wire order, continuity, and signal integrity.